World Hearing Day 2025 focuses on ear health and hearing loss prevention. Empower yourself and others for better ear care and hearing awareness.
World Hearing Day 2025 is an important event to raise awareness about hearing loss and ear health. The slogan for World Hearing Day is “Raise your voice for hearing health.” The theme for this year is “Changing mindsets: Empower yourself to make ear and hearing care a reality for all!” You can take steps today to ensure good hearing health throughout life, as recommended by the WHO.
Hearing loss occurs when you lose all or part of your hearing (usually in one ear) either suddenly or over the course of a few days. About half of those with the condition regain their hearing on their own, but sometimes it doesn’t come back completely.

Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis)
Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis):
Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis) is the gradual loss of hearing in both ears. It is a common problem linked to aging. About 1 in 3 adults between the ages of 65 and 74 experience hearing loss. This condition develops slowly over time. Age-related hearing loss, also called presbycusis, occurs gradually as a person grows older. It tends to run in families and may be caused by changes in the inner ear and auditory nerve, which relays signals from the ear to the brain.

Loud Noise
Loud Noise:
Loud noise is one of the most common causes of hearing loss. Noise from lawn mowers, snow blowers, or loud music can damage the inner ear and lead to permanent hearing loss. Loud noise also contributes to tinnitus. Sounds at or below 70 A-weighted decibels (dBA), even after long exposure, are unlikely to cause hearing loss. However, long or repeated exposure to sounds at or above 85 dBA can cause hearing loss. The louder the sound, the shorter the time it takes for Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL) to occur.

Ear Infections
Ear Infections:
An ear infection is caused by a bacterium or virus in the middle ear. This infection often results from another illness—such as a cold, flu, or allergy—that causes congestion and swelling in the nasal passages, throat, and eustachian tubes. There are different types of ear infections:
- Middle ear infection (acute otitis media): an infection in the middle ear.
- Otitis media with effusion: another condition affecting the middle ear.
- Swimmer’s ear: an infection in the outer ear canal.
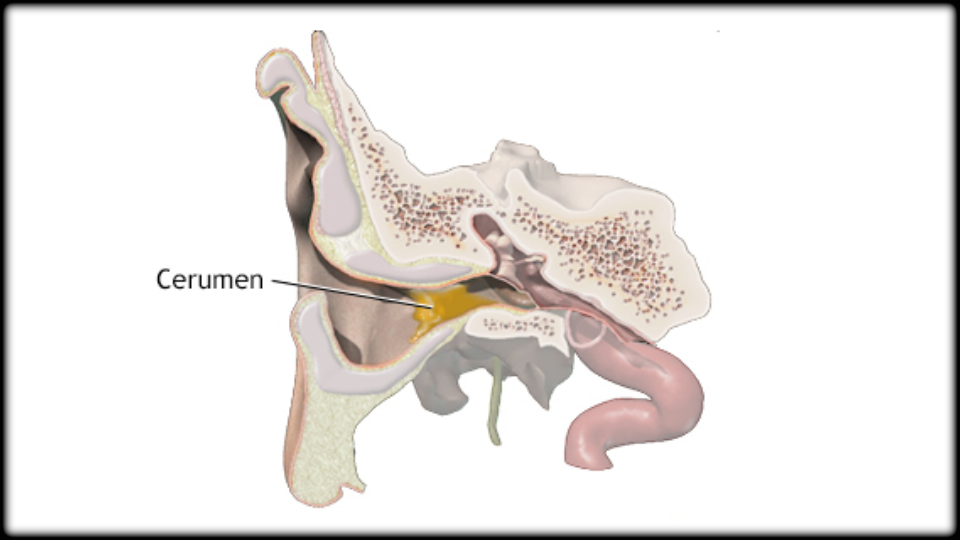
Earwax or Fluid Buildup
Earwax or Fluid Buildup:
A buildup of earwax can block sound from reaching the eardrum, causing temporary hearing impairment. If left untreated, excessive earwax may worsen symptoms such as hearing loss, ear irritation, tinnitus, and other issues. A buildup of earwax can also make it difficult to see into the ear, potentially leading to undiagnosed issues.
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Disease:
Cardiovascular disease is commonly thought to contribute to hearing loss due to compromised blood flow to the cochlea. This reduction may result from microvascular changes in the stria vascularis or macrovascular changes in the internal auditory artery. Cardiovascular disease puts increased strain on the heart and can lead to:
- Angina: chest pain caused by restricted blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Heart attacks: when blood flow to the heart muscle is suddenly blocked.
- Heart failure: when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively throughout the body.
Genetic Variations
Genetic Variations:
Hereditary conditions can lead to hearing loss either at birth or later in life. For example, a person who inherits two changed GJB2 genes (one from each parent) will have hearing loss. This means that if both parents carry a single changed GJB2 gene, they can have a child with hearing loss, even though both parents have normal hearing. In fact, most babies with hearing loss are born to parents who can hear.

Ruptured Eardrum
Ruptured Eardrum:
A ruptured eardrum, or perforated eardrum, usually heals on its own within 2 months if the hole is small. Hearing loss will typically be short-term if the rupture heals completely. However, in rare cases, other problems may occur, such as:
Long-term hearing loss.
- Increased vulnerability to middle ear infections.
- While a ruptured eardrum generally heals within a few weeks without treatment, it may sometimes require a patch or surgical repair.
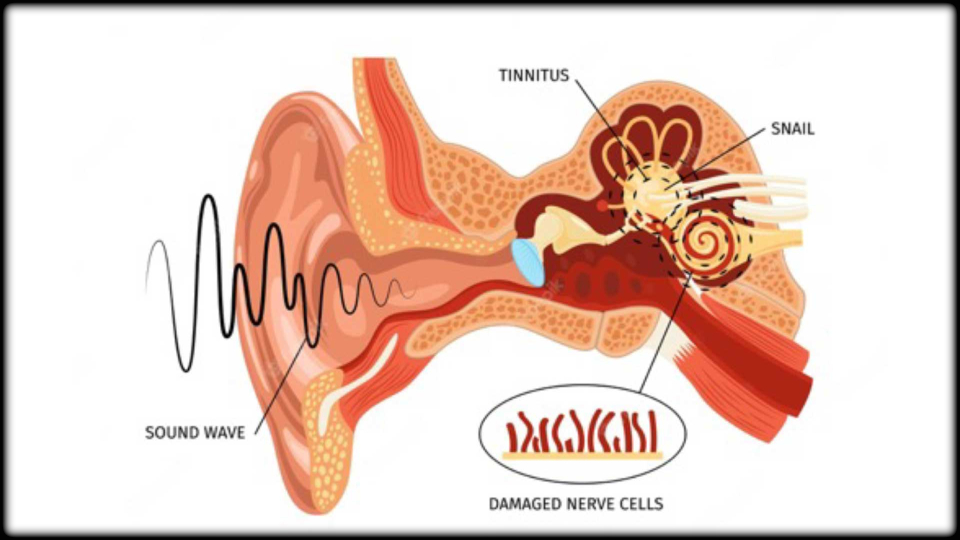
Tinnitus
Tinnitus:
Tinnitus is the perception of ringing or buzzing in the ears, often caused by damage to the auditory system. It is rarely associated with serious medical problems and is usually not severe enough to interfere with daily life. However, some people find that tinnitus affects their mood and their ability to sleep or concentrate. In severe cases, tinnitus can lead to anxiety or depression.

Trauma & Inflammation
Trauma & Inflammation:
Inflammation contributes to the pathogenesis of various types of Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL). Inflammation is a normal immune response, and a blind, systemic anti-inflammatory approach is undesirable. The external ear (pinna or auricle) can be damaged by trauma or inflammation. This can occur from direct injury to the outer ear or head, or from inserting foreign objects into the ear canal (e.g., matchsticks, hairpins), which may damage the ear canal skin or rupture the eardrum.
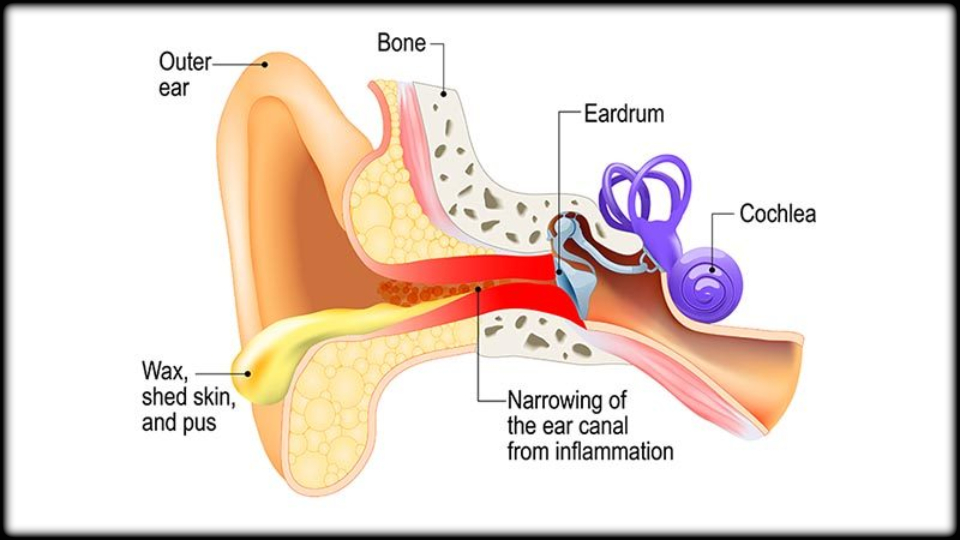
Otitis Externa
Otitis Externa:
Fluctuating conductive hearing loss almost always occurs with all types of otitis media. In fact, otitis media is the most common cause of hearing loss in young children. Otitis media is the most frequently diagnosed disease in infants and young children. Patients with otitis externa experience pain when manipulating the pinna or tragus, and their ear canal is swollen and filled with infectious debris. Conductive hearing loss may occur if swelling and debris block the ear canal.
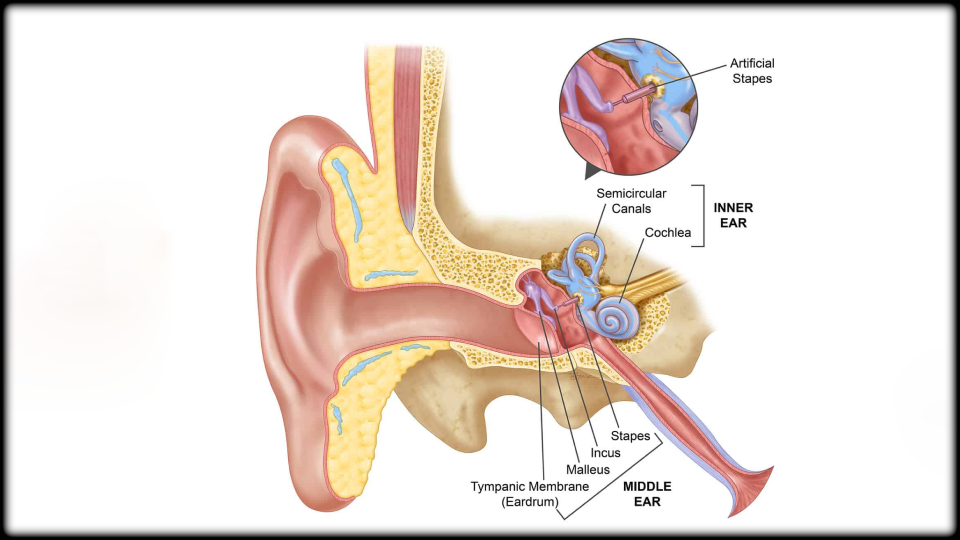
Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis:
Otosclerosis occurs when one of the bones in the middle ear, the stapes, becomes stuck in place. When this bone is unable to vibrate, sound cannot travel through the ear, resulting in hearing impairment. Otosclerosis is characterized by abnormal bone growth within the middle ear that prevents these tiny bones from vibrating. This causes hearing loss because the sound waves cannot reach the inner ear. The sense of balance may also be affected if the abnormal bone growth extends into the inner ear.














Pingback : World Hearing Day: Empowering Hearing Health for All